Overcoming water-related challenges is inseparable from tackling energy-related points. It takes plenty of water to generate vitality, for instance to chill thermal energy vegetation and nuclear reactors. Vitality, in flip, is required for water-related actions corresponding to drilling, transportation, purification, desalination, and wastewater therapy.
As a result of the connection between water and vitality is so shut and sophisticated, issues corresponding to entry, shortage, or mismanagement of 1 can considerably have an effect on the opposite. If water is scarce, this will hamper vitality manufacturing and hinder efforts to chop carbon emissions. And vitality manufacturing that ignores water limitations can result in air pollution, as seen in Shell’s oil operations in Nigeria, which have brought on extreme native injury. Likewise, fossil-fuel energy vegetation are main contributors to water air pollution, releasing contaminants that threaten public well being and ecosystems, together with rivers, groundwater, and surrounding communities.
Based on the Worldwide Vitality Company (IEA), world water withdrawals for electrical energy and gas manufacturing reached round 370 billion cubic metres in 2021. Most was used for cooling in thermal and nuclear energy vegetation. It’s projected that water withdrawals for vitality manufacturing may rise to 400 billion cubic metres by 2030.
Within the vitality sector, electrical energy technology accounts for the most important share of water withdrawals. In 2021, round 54 billion cubic metres of water had been used to supply vitality. Though in 2021 the worldwide vitality system used much less water than in 2010, it nonetheless accounts for roughly 10 % of complete world freshwater withdrawals.
In 2023, the United Nations Local weather Change Convention referred to as for world renewable vitality capability to be tripled by 2030. Reaching this objective would require including a mean of 1,100 gigawatts of renewable capability per 12 months. This holds out the hope of lowering the exploitation of the world’s water assets. Renewable vitality sources symbolize solely a small fraction of complete water consumption, a lot smaller than that of fossil fuel-based vitality.
Water drives generators and lights cities – but it additionally powers myths and religion, seen as near-omnipotent: capable of create, destroy, cleanse, and redeem. Credit: Eimermacher/stockmarpluswalter.
However vital challenges stay. The local weather disaster is disrupting the worldwide water cycle. The mining business is failing to handle its waste and cut back its consumption of water. Social and environmental issues abound. Many essential minerals lie in water-scarce areas, together with lithium, nickel, cobalt, and graphite for batteries, and uncommon earth parts for wind generators and electrical autos. Over 50 % of the world’s lithium reserves are positioned in water-scarce areas. Chile, the world’s largest copper producer, holds round 21 % of worldwide copper reserves. Mining poses vital environmental dangers, significantly to fragile forest ecosystems, because it requires giant quantities of water and pollutes each floor water and groundwater. Mineral extraction depends on chemical compounds that may be hazardous if not correctly managed, posing severe threats to human well being, biodiversity, and the surroundings.
So-called inexperienced hydrogen, or hydrogen produced by the electrolysis of water utilizing renewable electrical energy, is commonly held up as a substitute for fossil fuels. However producing one kilogram of hydrogen consumes between 9 and 13 kilograms of water; precise consumption could also be greater, relying on the electrolysis expertise and quantity of cooling water used. Desalination vegetation, which take away salt from saline water by filtering or heating, are increasing to fulfill demand. Most are within the Center East. However desalination is pricey, takes numerous vitality, and has huge environmental impacts. In lots of nations, solely wealthier areas or social teams can afford entry to desalinated water as a consequence of its excessive price, whereas poorer areas usually lack the infrastructure or funding – regardless of having equal and even larger water wants. It additionally generates huge quantities of brine waste – 141.5 million cubic metres per day – with 70 % of that within the Center East.
One other controversial water-intensive expertise is Carbon Seize and Storage (CCS). This entails capturing greenhouse fuel emissions from fossil-fuel energy vegetation and storing them underground. This takes numerous water. The big-scale growth of such applied sciences may practically double humanity’s water footprint.
Lowering vitality demand in a coordinated method is essential for making certain a good, safe, and sustainable future within the face of the local weather disaster and water shortage. A technique that integrates water-efficient vitality applied sciences is important for lowering strain on important water assets whereas offering equitable entry to vitality.
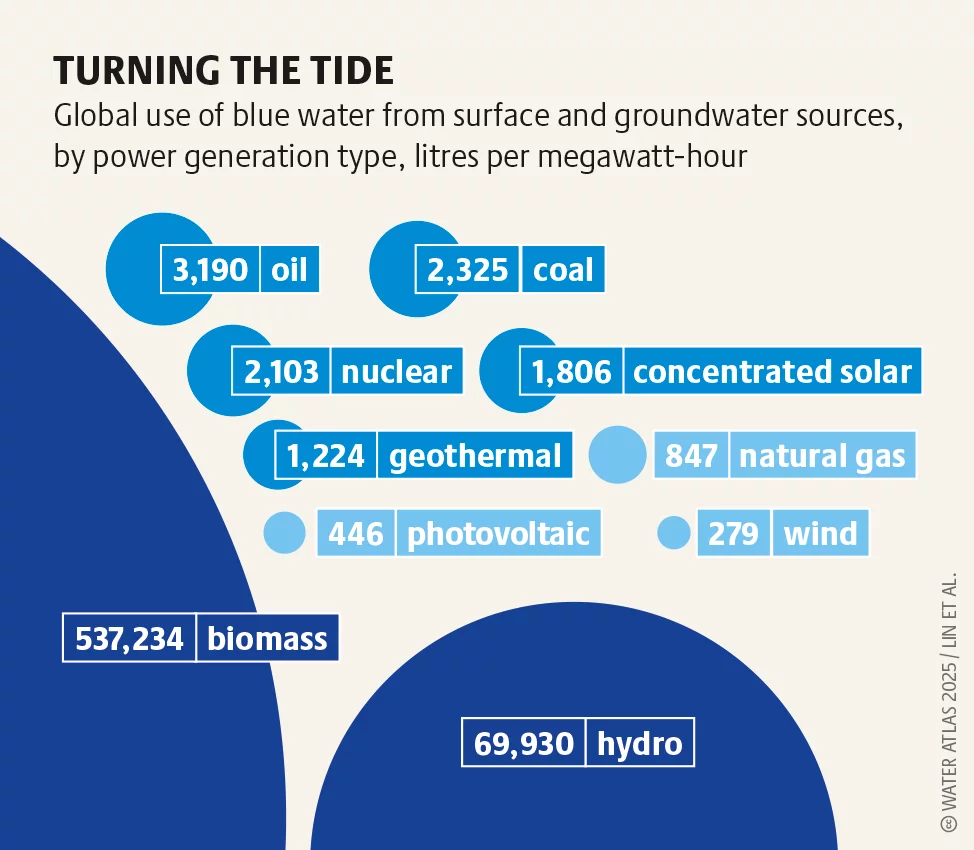
Fossil fuels hurt the local weather and eat a lot water. Renewables like photo voltaic and wind lower CO₂ emissions and use much less water. Credit: Eimermacher/stockmarpluswalter.
This text was first printed on eu.boell.org.
Learn extra of our Water Atlas right here.















